基于sharedLibrary进行CI/CD流程的优化
由于公司内部项目众多,大量的项目使用同一套流程做CICD
- 那么势必会存在大量的重复代码
- 一旦某个公共的地方需要做调整,每个项目都需要修改
因此本章主要通过使用groovy实现Jenkins的sharedLibrary的开发,以提取项目在CICD实践过程中的公共逻辑,提供一系列的流程的接口供公司内各项目调用。
开发完成后,对项目进行Jenkinsfile的改造,最后仅需通过简单的Jenkinsfile的配置,即可优雅的完成CICD流程的整个过程,此方式已在大型企业内部落地应用。
Library工作模式
由于流水线被组织中越来越多的项目所采用,常见的模式很可能会出现。 在多个项目之间共享流水线有助于减少冗余并保持代码 “DRY”。
流水线支持引用 “共享库” ,可以在外部源代码控制仓库中定义并加载到现有的流水线中。
@Library('my-shared-library') _
在实际运行过程中,会把library中定义的groovy功能添加到构建目录中:
/var/jenkins_home/jobs/test-maven-build/branches/feature-CDN-2904.cm507o/builds/2/libs/my-shared-library/vars/devops.groovy
使用library后,Jenkinsfile大致的样子如下:
@Library('my-shared-library') _
...
stages {
stage('build image') {
steps {
container('tools') {
devops.buildImage("Dockerfile","172.21.51.67:5000/demo:latest")
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
script {
container('tools') {
devops.notificationSuccess("dingTalk")
}
}
}
}
...
开发环境搭建
补录章节:Groovy及SpringBoot、SpringCloud都会使用
- java
- groovy
- intelliJ idea
下载安装包
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1B-bg2_IsB8dU7_62IEtnTg 提取码:wx6j
安装java
安装路径:D:\software\jdk
环境变量:
- JAVA_HOME D:\software\jdk
- CLASSPATH .;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\dt.jar;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar;
- PATH %JAVA_HOME%\bin
安装groovy
解压路径:D:\software\groovy-3.0.2
环境变量:
- GROOVY_PATH D:\software\groovy-3.0.2
- PATH D:\software\groovy-3.0.2\bin
安装idea
安装路径:D:\software\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2.3
新建项目测试
Library代码结构介绍
共享库的目录结构如下:
(root)
+- src # Groovy source files
| +- org
| +- foo
| +- Bar.groovy # for org.foo.Bar class
+- vars
| +- foo.groovy # for global 'foo' variable
| +- foo.txt # help for 'foo' variable
src 目录应该看起来像标准的 Java 源目录结构。当执行流水线时,该目录被添加到类路径下。
vars 目录定义可从流水线访问的全局变量的脚本。 每个 *.groovy 文件的基名应该是一个 Groovy (~ Java) 标识符, 通常是 camelCased。
Groovy基本语法介绍
新建Groovy项目
-
变量
使用数据类型的本地语法,或者使用def关键字
// Defining a variable in lowercase int x = 5; // Defining a variable in uppercase int X = 6; // Defining a variable with the underscore in it's name def _Name = "Joe"; println(x); println(X); println(_Name); -
方法
-
调用本地方法
def sum(int a, int b){ return a + b } println(sum(1,2)) -
调用类中的方法
# Hello.groovy package demo def sayHi(String content) { return ("hi, " + content) } # Demo.groovy import demo.Hello def demo() { return new Hello().sayHi("devops") } println(demo()) # 级联调用 # Hello.groovy package demo def init(String content) { this.content = content return this } def sayHi() { println("hi, " + this.content) return this } def sayBye() { println("bye " + this.content) } # Demo.groovy import demo.Hello def demo() { new Hello().init("devops").sayHi().sayBye() } demo()
-
-
异常捕获
def exceptionDemo(){ try { def val = 10 / 0 println(val) }catch(Exception e) { println(e.toString()) throw e } } exceptionDemo() -
计时器与循环
import groovy.time.TimeCategory use( TimeCategory ) { def endTime = TimeCategory.plus(new Date(), TimeCategory.getSeconds(15)) def counter = 0 while(true) { println(counter++) sleep(1000) if (new Date() >= endTime) { println("done") break } } } -
解析yaml文件
import org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml def readYaml(){ def content = new File('myblog.yaml').text Yaml parser = new Yaml() def data = parser.load(content) def kind = data["kind"] def name = data["metadata"]["name"] println(kind) println(name) } readYaml()
library与Jenkins集成
先来看一下如何使用shared library实现最简单的helloworld输出功能,来理清楚使用shared library的流程。
Hello.groovy
package com.luffy.devops
/**
* @author Yongxin
* @version v0.1
*/
/**
* say hello
* @param content
*/
def hello(String content) {
this.content = content
return this
}
def sayHi() {
echo "Hi, ${this.content},how are you?"
return this
}
def answer() {
echo "${this.content}: fine, thank you, and you?"
return this
}
def sayBye() {
echo "i am fine too , ${this.content}, Bye!"
return this
}
在gitlab创建项目,把library代码推送到镜像仓库。
配置Jenkins
[系统管理] -> [系统设置] -> [ Global Pipeline Libraries ]
- Library Name:luffy-devops
- Default Version:master
- Source Code Management:Git
Jenkinsfile中引用
jenkins/pipelines/p11.yaml
@Library('luffy-devops') _
pipeline {
agent { label 'jnlp-slave'}
stages {
stage('hello-devops') {
steps {
script {
devops.hello("树哥").sayHi().answer().sayBye()
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
echo 'Congratulations!'
}
failure {
echo 'Oh no!'
}
always {
echo 'I will always say Hello again!'
}
}
}
创建vars/devops.groovy
import com.luffy.devops.Hello
def hello(String content) {
return new Hello().hello(content)
}
library集成镜像构建及推送
需要实现的逻辑点:
- docker build,docker push,docker login
- 账户密码,jenkins凭据,(library中获取凭据内容),
- docker login 172.21.51.67:5000
- try catch
镜像构建逻辑实现
devops.groovy
/**
*
* @param repo, 172.21.51.67:5000/demo/myblog/xxx/
* @param tag, v1.0
* @param dockerfile
* @param credentialsId
* @param context
*/
def docker(String repo, String tag, String credentialsId, String dockerfile="Dockerfile", String context=".") {
return new Docker().docker(repo, tag, credentialsId, dockerfile, context)
}
Docker.groovy
逻辑中需要注意的点:
- 构建和推送镜像,需要登录仓库(需要认证)
- 构建成功或者失败,需要将结果推给gitlab端
- 为了将构建过程推送到钉钉消息中,需要将构建信息统一收集
package com.luffy.devops
/**
*
* @param repo
* @param tag
* @param credentialsId
* @param dockerfile
* @param context
* @return
*/
def docker(String repo, String tag, String credentialsId, String dockerfile="Dockerfile", String context="."){
this.repo = repo
this.tag = tag
this.dockerfile = dockerfile
this.credentialsId = credentialsId
this.context = context
this.fullAddress = "${this.repo}:${this.tag}"
this.isLoggedIn = false
return this
}
/**
* build image
* @return
*/
def build() {
this.login()
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker build ${this.context} -t ${this.fullAddress} -f ${this.dockerfile} "
}catch (Exception exc) {
throw exc
}
return this
}
}
/**
* push image
* @return
*/
def push() {
this.login()
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker push ${this.fullAddress}"
}catch (Exception exc) {
throw exc
}
}
return this
}
/**
* docker registry login
* @return
*/
def login() {
if(this.isLoggedIn || credentialsId == ""){
return this
}
// docker login
withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: this.credentialsId, usernameVariable: 'USERNAME', passwordVariable: 'PASSWORD')]) {
def regs = this.getRegistry()
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker login ${regs} -u $USERNAME -p $PASSWORD"
} catch (Exception exc) {
echo "docker login err, " + exc.toString()
}
}
}
this.isLoggedIn = true;
return this;
}
/**
* get registry server
* @return
*/
def getRegistry(){
def sp = this.repo.split("/")
if (sp.size() > 1) {
return sp[0]
}
return this.repo
}
Jenkinsfile
需要先在Jenkins端创建仓库登录凭据credential-registry
@Library('luffy-devops') _
pipeline {
agent { label 'jnlp-slave'}
options {
timeout(time: 20, unit: 'MINUTES')
gitLabConnection('gitlab')
}
environment {
IMAGE_REPO = "172.21.51.67:5000/demo/myblog"
IMAGE_CREDENTIAL = "credential-registry"
}
stages {
stage('checkout') {
steps {
container('tools') {
checkout scm
}
}
}
stage('docker-image') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.docker(
"${IMAGE_REPO}",
"${GIT_COMMIT}",
IMAGE_CREDENTIAL
).build().push()
}
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
echo 'Congratulations!'
}
failure {
echo 'Oh no!'
}
}
}
丰富构建通知逻辑
目前的构建镜像逻辑中缺少如下内容:
- try逻辑中,若发生异常,是否该把异常抛出
- 若直接抛出异常可能会导致多次重复的异常信息
- 若不抛出,则如果未构建成功镜像,流水线感知不到错误
- 通知gitlab端构建任务及状态
- 构建通知格式
需要针对上述问题,做出优化
-
优化try逻辑
def build() { this.login() def isSuccess = false def errMsg retry(3) { try { sh "docker build ${this.context} -t ${this.fullAddress} -f ${this.dockerfile}" isSuccess = true }catch (Exception err) { //ignore errMsg = err.toString() } // check if build success if(isSuccess){ //todo }else { // throw exception,aborted pipeline error errMsg } return this } } -
通知gitlab端构建任务及状态
def build() { this.login() def isSuccess = false def errMsg = "" retry(3) { try { sh "docker build ${this.context} -t ${this.fullAddress} -f ${this.dockerfile} " isSuccess = true }catch (Exception err) { //ignore errMsg = err.toString() } // check if build success def stage = env.STAGE_NAME + '-build' if(isSuccess){ updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: '${stage}', state: 'success') }else { updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: '${stage}', state: 'failed') // throw exception,aborted pipeline error errMsg } return this } } -
钉钉消息通知格式
由于每个stage都需要构建通知任务,因此抽成公共的逻辑,为各stage调用
BuildMessage.groovypackage com.luffy.devops def updateBuildMessage(String source, String add) { if(!source){ source = "" } env.BUILD_TASKS = source + add + "\n \n " return env.BUILD_TASKS }Docker.groovy中调用def getObject(String repo, String tag, String credentialsId, String dockerfile="Dockerfile", String context="."){ ... this.msg = new BuildMessage() return this } ... def build() { ... // check if build success def stage = env.STAGE_NAME + '-build' if(isSuccess){ updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: '${stage}', state: 'success') this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} OK... √") }else { updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: '${stage}', state: 'failed') this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} Failed... x") // throw exception,aborted pipeline error errMsg } return this } }
使用Jenkinsfile来验证上述修改是否正确:
@Library('luffy-devops') _
pipeline {
agent { label 'jnlp-slave'}
options {
timeout(time: 20, unit: 'MINUTES')
gitLabConnection('gitlab')
}
environment {
IMAGE_REPO = "172.21.51.67:5000/demo/myblog"
IMAGE_CREDENTIAL = "credential-registry"
DINGTALK_CREDS = credentials('dingTalk')
}
stages {
stage('checkout') {
steps {
container('tools') {
checkout scm
}
}
}
stage('git-log') {
steps {
script{
sh "git log --oneline -n 1 > gitlog.file"
env.GIT_LOG = readFile("gitlog.file").trim()
}
sh 'printenv'
}
}
stage('build-image') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.docker(
"${IMAGE_REPO}",
"${GIT_COMMIT}",
IMAGE_CREDENTIAL
).build().push()
}
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
sh """
curl 'https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=${DINGTALK_CREDS_PSW}' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"msgtype": "markdown",
"markdown": {
"title":"myblog",
"text": "😄👍 构建成功 👍😄 \n**项目名称**:luffy \n**Git log**: ${GIT_LOG} \n**构建分支**: ${BRANCH_NAME} \n**构建地址**:${RUN_DISPLAY_URL} \n**构建任务**:${env.BUILD_TASKS}"
}
}'
"""
}
failure {
echo 'Oh no!'
}
}
}
接下来需要将push和login方法做同样的改造
最终的Docker.groovy文件为:
package com.luffy.devops
/**
*
* @param repo
* @param tag
* @param credentialsId
* @param dockerfile
* @param context
* @return
*/
def docker(String repo, String tag, String credentialsId, String dockerfile="Dockerfile", String context="."){
this.repo = repo
this.tag = tag
this.dockerfile = dockerfile
this.credentialsId = credentialsId
this.context = context
this.fullAddress = "${this.repo}:${this.tag}"
this.isLoggedIn = false
this.msg = new BuildMessage()
return this
}
/**
* build image
* @return
*/
def build() {
this.login()
def isSuccess = false
def errMsg = ""
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker build ${this.context} -t ${this.fullAddress} -f ${this.dockerfile} "
isSuccess = true
}catch (Exception err) {
//ignore
errMsg = err.toString()
}
// check if build success
def stage = env.STAGE_NAME + '-build'
if(isSuccess){
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: "${stage}", state: 'success')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} OK... √")
}else {
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: "${stage}", state: 'failed')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} Failed... x")
// throw exception,aborted pipeline
error errMsg
}
return this
}
}
/**
* push image
* @return
*/
def push() {
this.login()
def isSuccess = false
def errMsg = ""
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker push ${this.fullAddress}"
isSuccess = true
}catch (Exception err) {
//ignore
errMsg = err.toString()
}
}
// check if build success
def stage = env.STAGE_NAME + '-push'
if(isSuccess){
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: "${stage}", state: 'success')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} OK... √")
}else {
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: "${stage}", state: 'failed')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} Failed... x")
// throw exception,aborted pipeline
error errMsg
}
return this
}
/**
* docker registry login
* @return
*/
def login() {
if(this.isLoggedIn || credentialsId == ""){
return this
}
// docker login
withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: this.credentialsId, usernameVariable: 'USERNAME', passwordVariable: 'PASSWORD')]) {
def regs = this.getRegistry()
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker login ${regs} -u $USERNAME -p $PASSWORD"
} catch (Exception ignored) {
echo "docker login err, ${ignored.toString()}"
}
}
}
this.isLoggedIn = true;
return this;
}
/**
* get registry server
* @return
*/
def getRegistry(){
def sp = this.repo.split("/")
if (sp.size() > 1) {
return sp[0]
}
return this.repo
}
再次测试构建
library集成k8s服务部署
library实现部署简单版
devops.groovy
/**
* kubernetes deployer
* @param resourcePath
*/
def deploy(String resourcePath){
return new Deploy().init(resourcePath)
}
新增Deploy.groovy
package com.luffy.devops
def init(String resourcePath){
this.resourcePath = resourcePath
this.msg = new BuildMessage()
return this
}
def start(){
try{
//env.CURRENT_IMAGE用来存储当前构建的镜像地址,需要在Docker.groovy中设置值
sh "sed -i 's#{{IMAGE_URL}}#${env.CURRENT_IMAGE}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
sh "kubectl apply -f ${this.resourcePath}"
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: env.STAGE_NAME, state: 'success')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${env.stage_name} OK... √")
} catch (Exception exc){
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: env.STAGE_NAME, state: 'failed')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${env.stage_name} fail... √")
throw exc
}
}
修改Docker.groovy
def push() {
this.login()
def isSuccess = false
def errMsg = ""
retry(3) {
try {
sh "docker push ${this.fullAddress}"
//把当前推送的镜像地址记录在环境变量中
env.CURRENT_IMAGE = this.fullAddress
isSuccess = true
}catch (Exception err) {
//ignore
errMsg = err.toString()
}
Jenkinsfile 中添加如下部分:
stage('deploy') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.deploy("deploy").start()
}
}
}
}
library实现自动部署优化版
简单版本最明显的问题就是无法检测部署后的Pod状态,如果想做集成测试,通常要等到最新版本的Pod启动后再开始。因此有必要在部署的时候检测Pod是否正常运行。
比如要去检查myblog应用的pod是否部署正常,人工检查的大致步骤:
-
kubectl -n luffy get pod,查看pod列表 -
找到列表中带有myblog关键字的running的pod
-
查看上述running pod数,是否和myblog的deployment中定义的replicas副本数一致
-
若一致,则检查结束,若不一致,可能稍等几秒钟,再次执行相同的检查操作
-
如果5分钟了还没有检查通过,则大概率是pod有问题,通过查看日志进一步排查
如何通过library代码实现上述过程:
-
library如何获取myblog的pod列表?
-
首先要知道本次部署的是哪个workload,因此需要调用者传递workload的yaml文件路径
-
library解析workload.yaml文件,找到如下值:
- pod所在的namespace
- pod中使用的
labels标签
-
使用如下命令查找该workload关联的pod
$ kubectl -n <namespace> get po -l <key1=value1> -l <key2=value2> # 如查找myblog的pod $ kubectl -n luffy get po -l app=myblog
-
-
如何确定步骤1中的pod的状态?
# 或者可以直接进行提取状态 $ kubectl -n luffy get po -l app=myblog -ojsonpath='{.items[0].status.phase}' # 以json数组的形式存储 $ kubectl -n luffy get po -l app=myblog -o json -
如何检测所有的副本数都是正常的?
# 以json数组的形式存储 $ kubectl -n luffy get po -l app=myblog -o json # 遍历数组,检测每一个pod查看是否均正常(terminating和evicted除外) -
如何实现在5分钟的时间内,若pod状态符合预期,则退出检测循环,若不符合预期则继续检测
use( TimeCategory ) { def endTime = TimeCategory.plus(new Date(), TimeCategory.getMinutes(timeoutMinutes,5)) while (true) { if (new Date() >= endTime) { //超时了,则宣告pod状态不对 updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: 'deploy', state: 'failed') throw new Exception("deployment timed out...") } //循环检测当前deployment下的pod的状态 try { if (this.isDeploymentReady()) { readyCount++ if(readyCount > 5){ updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: 'deploy', state: 'success') break; } }else { readyCount = 0 }catch (Exception exc){ echo exc.toString() } //每次检测若不满足所有pod均正常,则sleep 5秒钟后继续检测 sleep(5) } }
devops.groovy
通过添加参数 watch来控制是否在pipeline中观察pod的运行状态
/**
*
* @param resourcePath
* @param watch
* @param workloadFilePath
* @return
*/
def deploy(String resourcePath, Boolean watch = true, String workloadFilePath){
return new Deploy().init(resourcePath, watch, workloadFilePath)
}
完整版的Deploy.groovy
package com.luffy.devops
import org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml
import groovy.json.JsonSlurperClassic
import groovy.time.TimeCategory
def init(String resourcePath, Boolean watch, String workloadFilePath) {
this.resourcePath = resourcePath
this.msg = new BuildMessage()
this.watch = watch
this.workloadFilePath = workloadFilePath
if(!resourcePath && !workloadFilePath){
throw Exception("illegal resource path")
}
return this
}
def start(){
try{
sh "sed -i 's#{{IMAGE_URL}}#${env.CURRENT_IMAGE}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
sh "kubectl apply -f ${this.resourcePath}"
} catch (Exception exc){
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: env.STAGE_NAME, state: 'failed')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${env.stage_name} fail... √")
throw exc
}
if (this.watch) {
// 初始化workload文件
initWorkload()
String namespace = this.workloadNamespace
String name = env.workloadName
if(env.workloadType.toLowerCase() == "deployment"){
echo "begin watch pod status from deployment ${env.workloadName}..."
monitorDeployment(namespace, name)
}else {
//todo
echo "workload type ${env.workloadType} does not support for now..."
}
}else {
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: env.STAGE_NAME, state: 'success')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${env.STAGE_NAME} OK... √")
}
}
def initWorkload() {
try {
def content = readFile this.workloadFilePath
Yaml parser = new Yaml()
def data = parser.load(content)
def kind = data["kind"]
if (!kind) {
throw Exception("workload file ${kind} illegal, will exit pipeline!")
}
env.workloadType = kind
echo "${data}"
this.workloadNamespace = data["metadata"]["namespace"]
if (!this.workloadNamespace){
this.workloadNamespace = "default"
}
env.workloadName = data["metadata"]["name"]
} catch (Exception exc) {
echo "failed to readFile ${this.workloadFilePath},exception: ${exc}."
throw exc
}
}
/**
*
* @param namespace
* @param name
* @param timeoutMinutes
* @param sleepTime
* @return
*/
def monitorDeployment(String namespace, String name, int timeoutMinutes = 5, sleepTime = 3) {
def readyCount = 0
def readyTarget = 3
use( TimeCategory ) {
def endTime = TimeCategory.plus(new Date(), TimeCategory.getMinutes(timeoutMinutes))
def lastRolling
while (true) {
// checking timeout
if (new Date() >= endTime) {
echo "timeout, printing logs..."
this.printContainerLogs(lastRolling)
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: 'deploy', state: 'failed')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${env.STAGE_NAME} Failed... x")
throw new Exception("deployment timed out...")
}
// checking deployment status
try {
def rolling = this.getResource(namespace, name, "deployment")
lastRolling = rolling
if (this.isDeploymentReady(rolling)) {
readyCount++
echo "ready total count: ${readyCount}"
if (readyCount >= readyTarget) {
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: env.STAGE_NAME, state: 'success')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${env.STAGE_NAME} OK... √")
break
}
} else {
readyCount = 0
echo "reseting ready total count: ${readyCount},print pods event logs"
this.printContainerLogs(lastRolling)
sh "kubectl get pod -n ${namespace} -o wide"
}
} catch (Exception exc) {
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: 'deploy', state: 'failed')
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_RESULT, "${env.STAGE_NAME} Failed... ×")
echo "error: ${exc}"
}
sleep(sleepTime)
}
}
return this
}
def getResource(String namespace = "default", String name, String kind="deployment") {
sh "kubectl get ${kind} -n ${namespace} ${name} -o json > ${namespace}-${name}-yaml.yml"
def jsonStr = readFile "${namespace}-${name}-yaml.yml"
def jsonSlurper = new JsonSlurperClassic()
def jsonObj = jsonSlurper.parseText(jsonStr)
return jsonObj
}
def printContainerLogs(deployJson) {
if (deployJson == null) {
return;
}
def namespace = deployJson.metadata.namespace
def name = deployJson.metadata.name
def labels=""
deployJson.spec.template.metadata.labels.each { k, v ->
labels = "${labels} -l=${k}=${v}"
}
sh "kubectl describe pods -n ${namespace} ${labels}"
}
def isDeploymentReady(deployJson) {
def status = deployJson.status
def replicas = status.replicas
def unavailable = status['unavailableReplicas']
def ready = status['readyReplicas']
if (unavailable != null) {
return false
}
def deployReady = (ready != null && ready == replicas)
// get pod information
if (deployJson.spec.template.metadata != null && deployReady) {
if (deployJson.spec.template.metadata.labels != null) {
def labels=""
def namespace = deployJson.metadata.namespace
def name = deployJson.metadata.name
deployJson.spec.template.metadata.labels.each { k, v ->
labels = "${labels} -l=${k}=${v}"
}
if (labels != "") {
sh "kubectl get pods -n ${namespace} ${labels} -o json > ${namespace}-${name}-json.json"
def jsonStr = readFile "${namespace}-${name}-json.json"
def jsonSlurper = new JsonSlurperClassic()
def jsonObj = jsonSlurper.parseText(jsonStr)
def totalCount = 0
def readyCount = 0
jsonObj.items.each { k, v ->
echo "pod phase ${k.status.phase}"
if (k.status.phase != "Terminating" && k.status.phase != "Evicted") {
totalCount++;
if (k.status.phase == "Running") {
readyCount++;
}
}
}
echo "Pod running count ${totalCount} == ${readyCount}"
return totalCount > 0 && totalCount == readyCount
}
}
}
return deployReady
}
修改Jenkinsfile 调用部分:
stage('deploy') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.deploy("deploy", true, "deploy/deployment.yaml").start()
}
}
}
}
library实现即时消息推送
实现消息通知
由于发送消息通知属于通用的功能,因此有必要把消息通知抽象成为通用的功能。
devops.groovy
/**
* notificationSuccess
* @param project
* @param receiver
* @param credentialsId
* @param title
* @return
*/
def notificationSuccess(String project, String receiver="dingTalk", String credentialsId="dingTalk", String title=""){
new Notification().getObject(project, receiver, credentialsId, title).notification("success")
}
/**
* notificationFailed
* @param project
* @param receiver
* @param credentialsId
* @param title
* @return
*/
def notificationFailed(String project, String receiver="dingTalk", String credentialsId="dingTalk", String title=""){
new Notification().getObject(project, receiver, credentialsId, title).notification("failure")
}
新建Notification.groovy文件:
package com.luffy.devops
/**
*
* @param type
* @param credentialsId
* @param title
* @return
*/
def getObject(String project, String receiver, String credentialsId, String title) {
this.project = project
this.receiver = receiver
this.credentialsId = credentialsId
this.title = title
return this
}
def notification(String type){
String msg ="😄👍 ${this.title} 👍😄"
if (this.title == "") {
msg = "😄👍 流水线成功啦 👍😄"
}
// failed
if (type == "failure") {
msg ="😖❌ ${this.title} ❌😖"
if (this.title == "") {
msg = "😖❌ 流水线失败了 ❌😖"
}
}
String title = msg
// rich notify msg
msg = genNotificationMessage(msg)
if( this.receiver == "dingTalk") {
try {
//new DingTalk().markDown(title, msg, this.credentialsId)
} catch (Exception ignored) {}
}else if(this.receiver == "wechat") {
//todo
}else if (this.receiver == "email"){
//todo
}else{
error "no support notify type!"
}
}
/**
* get notification msg
* @param msg
* @return
*/
def genNotificationMessage(msg) {
// project
msg = "${msg} \n **项目名称**: ${this.project}"
// get git log
def gitlog = ""
try {
sh "git log --oneline -n 1 > gitlog.file"
gitlog = readFile "gitlog.file"
} catch (Exception ignored) {}
if (gitlog != null && gitlog != "") {
msg = "${msg} \n **Git log**: ${gitlog}"
}
// get git branch
def gitbranch = env.BRANCH_NAME
if (gitbranch != null && gitbranch != "") {
msg = "${msg} \n **Git branch**: ${gitbranch}"
}
// build tasks
msg = "${msg} \n **Build Tasks**: ${env.BUILD_TASKS}"
// get buttons
msg = msg + getButtonMsg()
return msg
}
def getButtonMsg(){
String res = ""
def buttons = [
[
"title": "查看流水线",
"actionURL": "${env.RUN_DISPLAY_URL}"
],
[
"title": "代码扫描结果",
"actionURL": "http://sonar.luffy.com/dashboard?id=${this.project}"
]
]
buttons.each() {
if(res == ""){
res = " \n >"
}
res = "${res} --- ["+it["title"]+"]("+it["actionURL"]+") "
}
return res
}
新建DingTalk.groovy文件:
package com.luffy.devops
import groovy.json.JsonOutput
def sendRequest(method, data, credentialsId, Boolean verbose=false, codes="100:399") {
def reqBody = new JsonOutput().toJson(data)
withCredentials([usernamePassword(credentialsId: credentialsId, usernameVariable: 'USERNAME', passwordVariable: 'PASSWORD')]) {
def response = httpRequest(
httpMode:method,
url: "https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=${PASSWORD}",
requestBody:reqBody,
validResponseCodes: codes,
contentType: "APPLICATION_JSON",
quiet: !verbose
)
}
}
def markDown(String title, String text, String credentialsId, Boolean verbose=false) {
def data = [
"msgtype": "markdown",
"markdown": [
"title": title,
"text": text
]
]
this.sendRequest("POST", data, credentialsId, verbose)
}
需要用到Http Request来发送消息,安装一下插件:http_request
jenkinsfile调用
@Library('luffy-devops') _
pipeline {
agent { label 'jnlp-slave'}
options {
timeout(time: 20, unit: 'MINUTES')
gitLabConnection('gitlab')
}
environment {
IMAGE_REPO = "172.21.51.67:5000/demo/myblog"
IMAGE_CREDENTIAL = "credential-registry"
DINGTALK_CREDS = credentials('dingTalk')
}
stages {
stage('checkout') {
steps {
container('tools') {
checkout scm
}
}
}
stage('docker-image') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.docker(
"${IMAGE_REPO}",
"${GIT_COMMIT}",
IMAGE_CREDENTIAL
).build().push()
}
}
}
}
stage('deploy') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.deploy("deploy",true,"deploy/deployment.yaml").start()
}
}
}
}
}
post {
success {
script{
devops.notificationSuccess("myblog","dingTalk")
}
}
failure {
script{
devops.notificationFailure("myblog","dingTalk")
}
}
}
}
library集成代码扫描
sonarqube代码扫描作为通用功能,同样可以使用library实现。
devops.groovy
/**
* sonarqube scanner
* @param projectVersion
* @param waitScan
* @return
*/
def scan(String projectVersion="", Boolean waitScan = true) {
return new Sonar().init(projectVersion, waitScan)
}
新建Sonar.groovy
- 可以传递projectVersion作为sonarqube的扫描版本
- 参数waitScan来设置是否等待本次扫描是否通过
package com.luffy.devops
def init(String projectVersion="", Boolean waitScan = true) {
this.waitScan = waitScan
this.msg = new BuildMessage()
if (projectVersion == ""){
projectVersion = sh(returnStdout: true, script: 'git log --oneline -n 1|cut -d " " -f 1')
}
sh "echo '\nsonar.projectVersion=${projectVersion}' >> sonar-project.properties"
sh "cat sonar-project.properties"
return this
}
def start() {
try {
this.startToSonar()
}
catch (Exception exc) {
throw exc
}
return this
}
def startToSonar() {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonarqube') {
sh "sonar-scanner -X;"
sleep 5
}
if(this.waitScan){
//wait 3min
timeout(time: 3, unit: 'MINUTES') {
def qg = waitForQualityGate()
String stage = "${env.stage_name}"
if (qg.status != 'OK') {
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, "${stage} Failed... ×")
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: "${stage}", state: 'failed')
error "Pipeline aborted due to quality gate failure: ${qg.status}"
}else{
this.msg.updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_RESULT, "${stage} OK... √")
updateGitlabCommitStatus(name: "${stage}", state: 'success')
}
}
}else{
echo "skip waitScan"
}
return this
}
Jenkinsfile新增如下部分:
stage('CI'){
failFast true
parallel {
stage('Unit Test') {
steps {
echo "Unit Test Stage Skip..."
}
}
stage('Code Scan') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script {
devops.scan().start()
}
}
}
}
}
}
集成robot自动化测试
关于集成测试,我们需要知道的几点:
- 测试人员进行编写
- 侧重于不同模块的接口调用,对新加的功能进行验证
- 注重新版本对以前的集成用例进行回归
因此,更多的应该是跨模块去测试,而且测试用例是测试人员去维护,因此不适合把代码放在开发的git仓库中。
本节要实现的工作:
- 创建新的git仓库
robot-cases,用于存放robot测试用例 - 为
robot-cases项目创建Jenkinsfile - 配置Jenkins任务,实现该项目的自动化执行
- 在myblog模块的流水线中,对该流水线项目进行调用
初始化robot-cases项目
-
新建gitlab项目,名称为
robot-cases -
clone到本地
-
本地拷贝myblog项目的
robot.txtrobot-cases/ └── myblog └── robot.txt
配置Jenkinsfile及自动化任务
robot-cases/
├── Jenkinsfile
└── myblog
└── robot.txt
Jenkinsfile
多个业务项目的测试用例都在一个仓库中,因此需要根据参数设置来决定执行哪个项目的用例
pipeline {
agent {
label 'jnlp-slave'
}
options {
timeout(time: 20, unit: 'MINUTES')
gitLabConnection('gitlab')
}
stages {
stage('checkout') {
steps {
container('tools') {
checkout scm
}
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
script {
container('tools'){
switch(env.comp){
case "myblog":
env.testDir = "myblog"
break
case "business1":
env.testDir = "business1"
break
default:
env.testDir = "all"
break
}
sh 'robot -d artifacts/ ${testDir}/*'
step([
$class : 'RobotPublisher',
outputPath: 'artifacts/',
outputFileName : "output.xml",
disableArchiveOutput : false,
passThreshold : 100,
unstableThreshold: 80.0,
onlyCritical : true,
otherFiles : "*.png"
])
archiveArtifacts artifacts: 'artifacts/*', fingerprint: true
}
}
}
}
}
}
如何实现将env.comp 传递进去?
配置流水线的参数化构建任务并验证参数化构建
library集成触发任务
由于多个项目均需要触发自动构建,因此可以在library中抽象方法,实现接收comp参数,并在library中实现对robot-cases项目的触发。
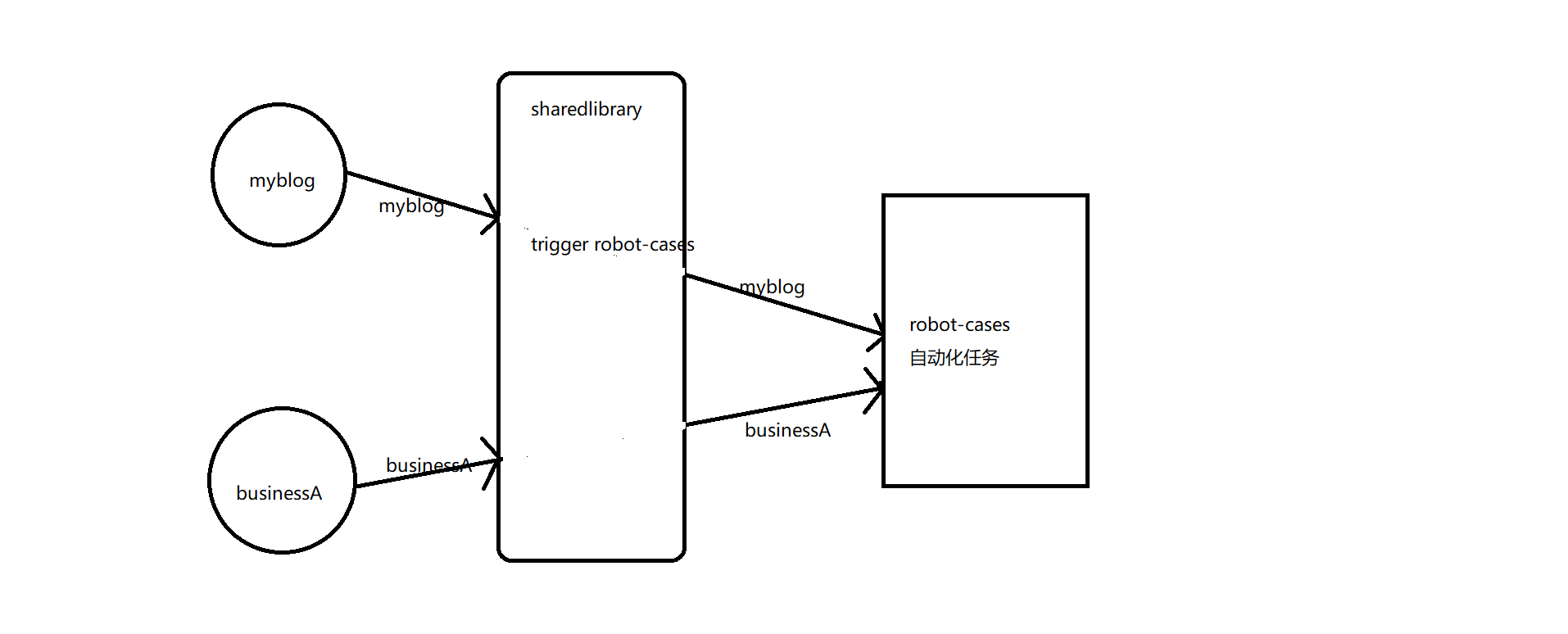
devops.groovy
/**
*
* @param comp
* @return
*/
def robotTest(String comp=""){
new Robot().acceptanceTest(comp)
}
新建Robot.groovy文件
package com.luffy.devops
def acceptanceTest(comp) {
try{
echo "Trigger to execute Acceptance Testing"
def rf = build job: 'robot-cases',
parameters: [
string(name: 'comp', value: comp)
],
wait: true,
propagate: false
def result = rf.getResult()
def msg = "${env.STAGE_NAME}... "
if (result == "SUCCESS"){
msg += "√ success"
}else if(result == "UNSTABLE"){
msg += "⚠ unstable"
}else{
msg += "× failure"
}
echo rf.getAbsoluteUrl()
env.ROBOT_TEST_URL = rf.getAbsoluteUrl()
new BuildMessage().updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_TASKS, msg)
} catch (Exception exc) {
echo "trigger execute Acceptance Testing exception: ${exc}"
new BuildMessage().updateBuildMessage(env.BUILD_RESULT, msg)
}
}
修改Jenkinsfile测试调用
stage('integration test') {
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.robotTest("myblog")
}
}
}
}
多环境的CICD自动化实现
实现目标及效果
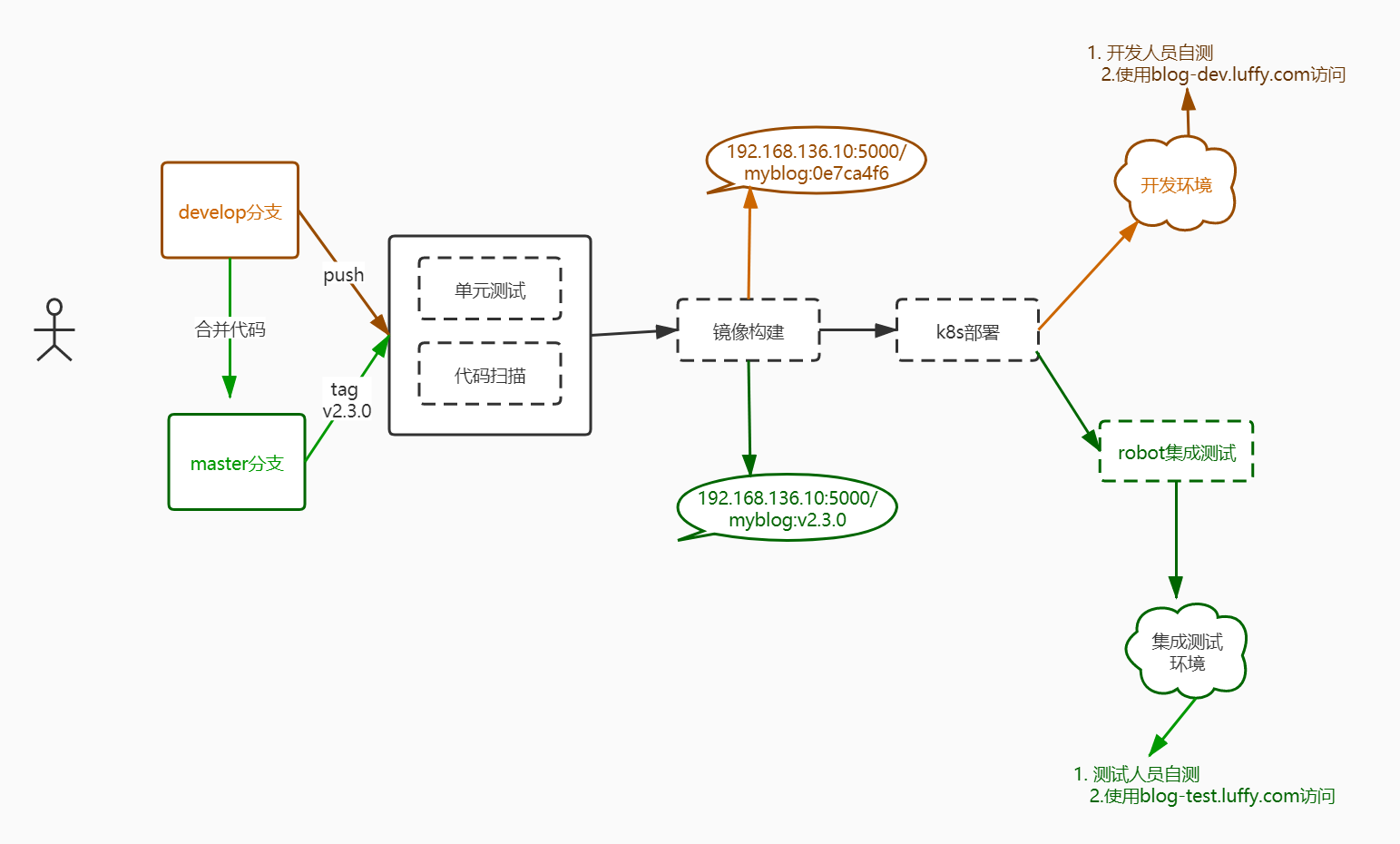
目前项目存在develop和master两个分支,Jenkinsfile中配置的都是构建部署到相同的环境,实际的场景中,代码仓库的项目往往不同的分支有不同的作用,我们可以抽象出一个工作流程:
-
开发人员提交代码到develop分支
-
Jenkins自动使用develop分支做单测、代码扫描、镜像构建(以commit id为镜像tag)、服务部署到开发环境
-
开发人员使用开发环境自测
-
测试完成后,在gitlab提交merge request请求,将代码合并至master分支
-
需要发版时,在gitlab端基于master分支创建tag(v2.3.0)
-
Jenkins自动检测到tag,拉取tag关联的代码做单测、代码扫描、镜像构建(以代码的tag为镜像的tag)、服务部署到测试环境、执行集成测试用例,输出测试报告
-
测试人员进行手动测试
-
上线
实现思路
以myblog项目为例,目前已经具备的是develop分支代码提交后,可以自动实现:
- 单元测试、代码扫描
- 镜像构建
- k8s服务部署
- robot集成用例测试
和上述目标相比,差异点:
- myblog应用目前只有一套环境,在luffy命名空间中。我们新建两个命名空间:
- dev,用作部署开发环境
- test,用作部署集成测试环境
- 需要根据不同的分支来执行不同的任务,有两种方案实现:
- develop和master分支使用不同的Jenkinsfile
- 可行性很差,因为代码合并工作很繁琐
- 维护成本高,多个分支需要维护多个Jenkinsfile
- 使用同一套Jenkinsfile,配合library和模板来实现一套Jenkinsfile适配多套环境
- 改造Jenkinsfile,实现根据分支来选择任务
- 需要将deploy目录中所有和特定环境绑定的内容模板化
- 在library中实现根据不同的分支,来替换模板中的内容
- develop和master分支使用不同的Jenkinsfile
Jenkinsfile根据分支选择任务
使用when关键字,配合正则表达式,实现分支的过滤选择:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ "develop" }
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying to develop env'
}
}
}
}
分别在develop和master分支进行验证。
针对本例,可以对Jenkinsfile做如下调整:
...
stage('integration test') {
when {
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ /v.*/ }
}
steps {
container('tools') {
script{
devops.robotTest(PROJECT)
}
}
}
}
...
模板化k8s的资源清单
因为需要使用同一套模板和Jenkinsfile来部署到不同的环境,因此势必要对资源清单进行模板化,前面的内容中只将deployment.yaml放到了项目的deploy清单目录,此处将部署myblog用到的资源清单均补充进去,包含:
- deployment.yaml
- service.yaml
- ingress.yaml
- configmap.yaml
- secret.yaml
涉及到需要进行模板化的内容包括:
-
镜像地址
-
命名空间
-
ingress的域名信息
模板化后的文件:
$ cat deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myblog
namespace: {{NAMESPACE}}
spec:
replicas: 1 #指定Pod副本数
selector: #指定Pod的选择器
matchLabels:
app: myblog
template:
metadata:
labels: #给Pod打label
app: myblog
spec:
containers:
- name: myblog
image: {{IMAGE_URL}}
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: MYSQL_HOST
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: myblog
key: MYSQL_HOST
- name: MYSQL_PORT
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: myblog
key: MYSQL_PORT
- name: MYSQL_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: myblog
key: MYSQL_USER
- name: MYSQL_PASSWD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: myblog
key: MYSQL_PASSWD
ports:
- containerPort: 8002
resources:
requests:
memory: 100Mi
cpu: 50m
limits:
memory: 500Mi
cpu: 100m
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /blog/index/
port: 8002
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10 # 容器启动后第一次执行探测是需要等待多少秒
periodSeconds: 15 # 执行探测的频率
timeoutSeconds: 2 # 探测超时时间
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /blog/index/
port: 8002
scheme: HTTP
initialDelaySeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 2
periodSeconds: 15
$ cat configmap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
MYSQL_HOST: mysql
MYSQL_PORT: "3306"
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: myblog
namespace: {{NAMESPACE}}
$ cat secret.yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
MYSQL_PASSWD: MTIzNDU2
MYSQL_USER: cm9vdA==
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: myblog
namespace: {{NAMESPACE}}
type: Opaque
$ cat service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: myblog
namespace: {{NAMESPACE}}
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8002
selector:
app: myblog
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
$ cat ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: myblog
namespace: {{NAMESPACE}}
spec:
rules:
- host: {{INGRESS_MYBLOG}}
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: myblog
servicePort: 80
path: /
status:
loadBalancer: {}
实现library配置替换逻辑
我们需要实现使用相同的模板,做到如下事情:
- 根据代码分支来部署到不同的命名空间
- develop分支部署到开发环境,使用命名空间 dev
- v.*部署到测试环境,使用命名空间 test
- 不同环境使用不同的ingress地址来访问
- 开发环境,
blog-dev.luffy.com - 测试环境,
blog-test.luffy.com
- 开发环境,
如何实现?sharedlibrary
所有的逻辑都会经过library这一层,我们具有完全可控权。
前面已经替换过镜像地址了,我们只需要实现如下逻辑:
- 检测当前代码分支,替换命名空间
- 检测当前代码分支,替换Ingress地址
问题来了,如何检测构建的触发是develop分支还是tag分支?
答案是:env.TAG_NAME,由tag分支触发的构建,环境变量中会带有TAG_NAME,且值为gitlab中的tag名称。
做个演示:
使用如下的Jenkinsfile,查看由master分支触发和由tag分支触发,printenv的值有什么不同
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Example Build') {
steps {
echo 'Hello World'
sh 'printenv'
}
}
stage('Example Deploy') {
when {
expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ "develop" }
}
steps {
echo 'Deploying to develop env'
}
}
}
}
我们可以选择和替换image镜像地址一样,来执行替换:
def tplHandler(){
sh "sed -i 's#{{IMAGE_URL}}#${env.CURRENT_IMAGE}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
String namespace = "dev"
String ingress = "blog-dev.luffy.com"
if(env.TAG_NAME){
namespace = "test"
ingress = "blog-test.luffy.com"
}
sh "sed -i 's#{{NAMESPACE}}#${namespace}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
sh "sed -i 's#{{INGRESS_MYBLOG}}#${ingress}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
}
但是我们的library是要为多个项目提供服务的,如果采用上述方式,则每加入一个项目,都需要对library做改动,形成了强依赖。因此需要想一种更优雅的方式来进行替换。
思路:
-
开发环境和集成测试环境里准备一个configmap,取名为
devops-config -
configmap的内容大致如下:
-
开发环境
NAMESPACE=dev INGRESS_MYBLOG=blog-dev.luffy.com -
测试环境
NAMESPACE=test INGRESS_MYBLOG=blog-test.luffy.com
-
-
约定:configmap的key值,拼接{{KEY}}则为代码中需要替换的模板部分,configmap的该key对应的value,则为该模板要被替换的值的内容。比如:
NAMESPACE=dev INGRESS_MYBLOG=blog-dev.luffy.com {{NAMESPACE}} => dev {{INGRESS_MYBLOG}} -> blog-dev.luffy.com意思是约定项目的deploy的资源清单中:
- 所有的
{{NAMESPACE}}被替换为dev - 所有的
{{INGRESS_MYBLOG}}被替换为blog-dev.luffy.com
- 所有的
-
在library的逻辑中,实现读取触发当前构建的代码分支所关联的namespace下的
devops-config这个configmap,然后遍历里面的值进行模板替换即可。
这样,则以后再有新增的项目,则只需要维护devops-config配置文件即可,shared-library则不需要随着项目的增加而进行修改,通过这种方式实现library和具体的项目解耦。
def tplHandler(){
sh "sed -i 's#{{IMAGE_URL}}#${env.CURRENT_IMAGE}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
String namespace = "dev"
if(env.TAG_NAME){
namespace = "test"
}
try {
def configMapData = this.getResource(namespace, "devops-config", "configmap")["data"]
configMapData.each { k, v ->
echo "key is ${k}, val is ${v}"
sh "sed -i 's#{{${k}}}#${v}#g' ${this.resourcePath}/*"
}
}catch (Exception exc) {
echo "failed to get devops-config data,exception: ${exc}."
throw exc
}
}
准备多环境
-
创建开发和测试环境的命名空间
# $ kubectl create namespace dev $ kubectl create namespace test -
分别在dev和test命名空间准备mysql数据库。演示功能,因此mysql未作持久化
$ cat mysql-all.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mysql namespace: dev spec: ports: - port: 3306 protocol: TCP targetPort: 3306 selector: app: mysql type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: myblog namespace: dev type: Opaque data: MYSQL_USER: cm9vdA== MYSQL_PASSWD: MTIzNDU2 --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mysql namespace: dev spec: replicas: 1 #指定Pod副本数 selector: #指定Pod的选择器 matchLabels: app: mysql template: metadata: labels: #给Pod打label app: mysql spec: containers: - name: mysql image: 172.21.51.67:5000/mysql:5.7-utf8 ports: - containerPort: 3306 env: - name: MYSQL_USER valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: myblog key: MYSQL_USER - name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: myblog key: MYSQL_PASSWD - name: MYSQL_DATABASE value: "myblog" resources: requests: memory: 100Mi cpu: 50m limits: memory: 500Mi cpu: 100m readinessProbe: tcpSocket: port: 3306 initialDelaySeconds: 5 periodSeconds: 10 # 创建开发环境的数据库 $ kubectl create -f mysql-all.yaml # 替换dev命名空间,创建测试环境的数据库 $ sed -i 's/namespace: dev/namespace: test/g' mysql-all.yaml $ kubectl create -f mysql-all.yaml -
对myblog项目的k8s资源清单模板化改造
- {{NAMESPACE}}
- {{INGRESS_MYBLOG}}
- {{IMAGE_URL}}
-
初始化开发环境和测试环境的
devops-config# 开发环境 $ cat devops-config-dev.txt NAMESPACE=dev INGRESS_MYBLOG=blog-dev.luffy.com $ kubectl -n dev create configmap devops-config --from-env-file=devops-config-dev.txt # 测试环境 $ cat devops-config-test.txt NAMESPACE=test INGRESS_MYBLOG=blog-test.luffy.com $ kubectl -n test create configmap devops-config --from-env-file=devops-config-test.txt -
提交最新的library代码
-
提交最新的python-demo项目代码
@Library('luffy-devops') _ pipeline { agent { label 'jnlp-slave'} options { timeout(time: 20, unit: 'MINUTES') gitLabConnection('gitlab') } environment { IMAGE_REPO = "172.21.51.67:5000/myblog" IMAGE_CREDENTIAL = "credential-registry" DINGTALK_CREDS = credentials('dingTalk') PROJECT = "myblog" } stages { stage('checkout') { steps { container('tools') { checkout scm } } } stage('CI'){ failFast true parallel { stage('Unit Test') { steps { echo "Unit Test Stage Skip..." } } stage('Code Scan') { steps { container('tools') { script { devops.scan().start() } } } } } } stage('docker-image') { steps { container('tools') { script{ devops.docker( "${IMAGE_REPO}", "${GIT_COMMIT}", IMAGE_CREDENTIAL ).build().push() } } } } stage('deploy') { steps { container('tools') { script{ devops.deploy("deploy",true,"deploy/deployment.yaml").start() } } } } stage('integration test') { when { expression { BRANCH_NAME ==~ /v.*/ } } steps { container('tools') { script{ devops.robotTest(PROJECT) } } } } } post { success { script{ devops.notificationSuccess(PROJECT,"dingTalk") } } failure { script{ devops.notificationFailure(PROJECT,"dingTalk") } } } }
验证多环境自动部署
模拟如下流程:
-
提交代码到develop分支,观察是否部署到dev的命名空间中,注意,第一次部署,需要执行migrate操作:
$ kubectl -n dev exec myblog-9f9f7c8cd-k6tbj python3 manage.py migrate -
配置hosts解析,测试使用
http://blog-dev.luffy.com/blog/index/进行访问到develop分支最新版本 -
合并代码至master分支
-
在gitlab中创建tag,观察是否自动部署至test的命名空间中,且使用
myblog-test.luffy.com/blog/index/可以访问到最新版本
实现打tag后自动部署
我们发现,打了tag以后,多分支流水线中可以识别到该tag,但是并不会自动部署该tag的代码。因此,我们来使用一个新的插件:Basic Branch Build Strategies Plugin
安装并配置多分支流水线,注意Build strategies 设置:
- Regular branches
- Tags
- Ignore tags newer than 可以不用设置,不然会默认不自动构建新打的tag
- Ignore tags older than
优化镜像部署逻辑
针对部署到测试环境的代码,由于已经打了tag了,因此,我们期望构建出来的镜像地址可以直接使用代码的tag作为镜像的tag。
思路一:直接在Jenkinsfile调用devops.docker时传递tag名称
思路二:在shared-library中,根据env.TAG_NAME来判断当前是否是tag分支的构建,若TAG_NAME不为空,则可以在构建镜像时使用TAG_NAME作为镜像的tag
很明显我们更期望使用思路二的方式来实现,因此,需要调整如下逻辑:
def docker(String repo, String tag, String credentialsId, String dockerfile="Dockerfile", String context="."){
this.repo = repo
this.tag = tag
if(env.TAG_NAME){
this.tag = env.TAG_NAME
}
this.dockerfile = dockerfile
this.credentialsId = credentialsId
this.context = context
this.fullAddress = "${this.repo}:${this.tag}"
this.isLoggedIn = false
this.msg = new BuildMessage()
return this
}
提交代码,并进行测试,观察是否使用tag作为镜像标签进行部署。
小结
Jenkins-shared-library的代码地址: https://gitee.com/agagin/jenkins-shared-library
目标:让devops流程更好用
- 项目更简便的接入
- devops流程更方便维护
思路:把各项目中公用的逻辑,抽象成方法,放到独立的library项目中,在各项目中引入shared-library项目,调用library提供的方法。
- 镜像构建、推送
- k8s服务部署、监控
- 钉钉消息推送
- 代码扫描
- robot集成测试
为了兼容多环境的CICD,因此采用模板与数据分离的方式,项目中的定义模板,shared-library中实现模板替换。为了实现shared-library与各项目解耦,使用configmap来维护模板与真实数据的值,思路是约定大于配置。